Are you looking for an easy way to explain the concept of simple present tense? Understanding how to use simple present tense correctly can be confusing for many people.
In this blog, we will discuss how to use simple present tense, with examples to help you understand. We will also look at how to form simple present tense sentences and how to use it in everyday conversations. By the end of this blog, you will have a better understanding of how to use simple present tense.
Contents
Rules for using simple present tense
The simple present tense is one of the most common verb tenses used in English. It is important for students to understand how to use this tense for clarity and accuracy in communication. In this blog, we will discuss the rules for conjugating verbs in the simple present tense, provide examples, and explain the differences between other verb tenses.
To begin, what is the simple present tense? The simple present tense is used to describe habits and routines, general truths, facts, and to express the future with more certainty (the definite future).
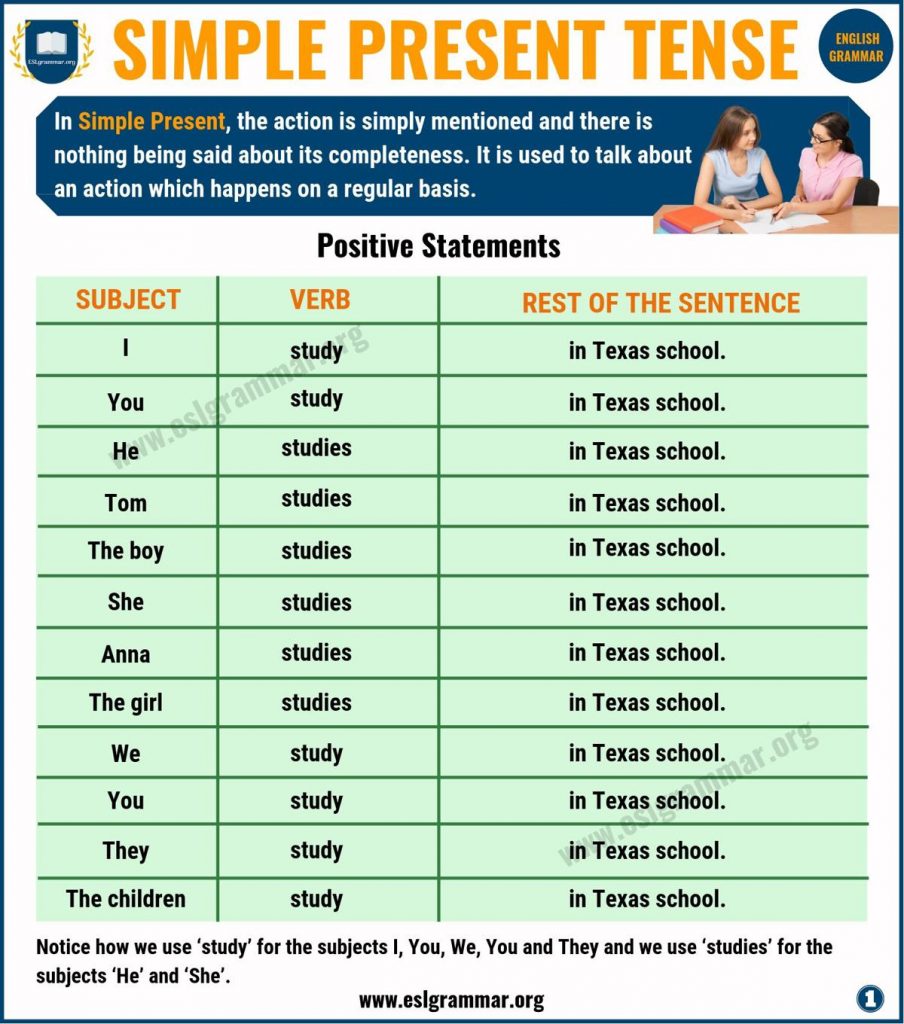
It is a verb tense that describes an action that is ongoing in the present. In order to conjugate a verb in the simple present tense, we must drop the verb’s -ing ending and then add one of the following endings: -s, -es, -ies, or -es.
For example, the verb “to study” becomes “studies” in the simple present tense, and the verb “to go” becomes “goes”. Next, when should we use the simple present tense? Most commonly, the simple present tense is used to talk about routines and habits.
For example, “He wakes up every morning at 6 am” or “I always have breakfast before going to work. ” It is also important to note that the simple present tense is used to talk about general truths and facts, such as “Cats have nine lives” or “The sun rises in the East. ” Finally, the simple present tense is used to express the future with more certainty.
For example, “I fly to Paris in two weeks” or “The movie starts tomorrow at 4 pm. ”In conclusion, the simple present tense is a useful verb tense for expressing general truths, talking about routines and habits, and expressing the future with more certainty.
Knowing how to use and conjugate the simple present tense is essential to effective communication in English. Students can practice and become comfortable with the simple present tense by creating sentences with the verbs they already know, then conjugating them into the simple present tense. In this way, they can apply what they have learned and build their fluency in English.
Examples of simple present tense
The simple present tense is one of the easiest tenses to learn and use in the English . As its name suggests, it is used to describe an action that is happening in the present.
Typically, the simple present tense is used for habitual or everyday activities, to describe situations that are permanent, or to make generalizations about things. For example, something might be “true in general” or “contrary to fact”. Using the simple present tense is fairly straightforward.
It consists of two parts – the basic verb and the subject: Verb + Subject. For example, the sentence “I love chocolate” is written in the simple present tense because it is an affirmative statement, where I is the subject and love is the verb.
Furthermore, the verb love does not have an ending, so it is an “uninflected” verb. When using the simple present tense, the verb itself does not change, even when the subject does. Therefore, the verb will remain the same whether it is I, you, he, she, or it.
For example, the sentence “I like chocolate” can also be written as “He likes chocolate”, where the verb is the same but the subject has changed. In conclusion, understanding and using the simple present tense can go a long way in helping English learners to communicate more clearly and accurately.
With a little practice and repetition, the simple present tense can become second nature and can be used in sentences without having to think too much about it.
Common mistakes to avoid when using simple present tense
The simple present is the most basic form of verb tenses. It is used to describe habitual actions, unchanging situations, and universal truths. While mastering the simple present is essential in conversational English, it can be difficult to master the nuances of it.
Without proper understanding and usage of the simple present, you can quickly fall into common pitfalls. From misplacing articles to incorrect verb tense usage, these mistakes can give your English an unprofessional feel and make comprehension difficult for the listener.
The first pitfall to avoid is forgetting to use the present tense. This is a common habit, especially when referring to future events or past actions. For example, if you want to say that you’re going to the concert tomorrow, you should say “I am going to the concert tomorrow.
” Similarly, if you want to talk about what you did yesterday, you should use the past tense and say “I went to the concert yesterday. ” It is important to remember that the present tense always describes something that is happening now, or in the very near future.
The second common mistake with the simple present is Mishandling Subject-Verb Agreement, as often seen with irregular verbs. When using the simple present, the subject and the verb need to agree, which can be tricky with irregular verbs. For example, the verb “to be” has different forms for each pronoun, such as “I am” and “he/she/it is.
” Thus, it is important to know all the forms for the different pronouns. Additionally, you need to remember to use the singular forms of irregular verbs when speaking about single subjects and the plural forms when speaking about multiple subjects.
The last major pitfall to watch out for when using the simple present is incorrectly placing articles. Articles are small words like “a,” “an,” and “the” that are used to give a phrase more detail. For example, the phrase “the big dog” tells us a bit more than just “big dog,” as it indicates that the listener should be looking for a specific big dog. Unfortunately, it is very easy to make mistakes when using articles, especially if the listener is a native English speaker. To help with this, it is important to remember that most singular nouns take a definite article (“the”) unless they are being used in an absolute sense, while most plural nouns take an indefinite article (“a” or “an”). To sum up, mastering the simple present can take time, but with practice, it can be done. To ensure you’re correctly using the simple present, be sure to avoid the common mistakes of not using the present tense, mishandling subject verb agreement, and incorrectly placing articles. For extra help, practice writing and conversing with native English speakers to help perfect your usage.
Tips for using simple present tense
The simple present tense is the basic tense in English grammar, used in everyday conversations and writings for habitual actions, routines, and general truths. It is a great tool for conveying your thoughts, feelings, opinions and ideas in a concise, efficient manner. Using the simple present tense doesn’t have to be tricky.
There are a few basic rules that you should be aware of – for example, the verb usually takes the same form as the third-person singular (he, she, it). In other words, if the subject is “I” you would use the verb in its present form (e.
g. I work) and if the subject is “he” you would use the third-person singular form (e. g.
he works). In addition, there are a few other points to consider; the present tense can be used to express both habits and facts, so try to be as specific as possible when constructing your sentences.
For example, if you want to talk about something which you do every day, use the present simple (e. g. I go to school); if you want to talk about a fact which is always true, use the present simple (e.
g. Earth orbits the sun).
Finally, don’t forget that the present simple tense can also be used to indicate future events – for example, “I’m going to the shop tomorrow” or “We’re leaving for Italy next Monday”. With practice and a few simple rules, you can master the simple present tense and use it in your everyday conversations and writings.
Our video recommendation
Conclusion
The simple present tense is used to describe habits, unchanging situations, general truths, and fixed arrangements. It is used to talk about facts, not opinions. Examples of sentences using the simple present tense are: “I go to school every day,” “She speaks two s,” and “It rains a lot in the winter.
” The simple present tense is an important part of English grammar and is used in everyday speech and writing.
FAQ
What is the simple present tense?
The simple present tense is a verb tense used to express an action or state of being that occurs in the present moment or is happening now.
How is the simple present tense used?
The simple present tense is used to describe habits, unchanging situations, general truths, and fixed arrangements. It is also used to talk about scheduled future events.
What are some examples of the simple present tense?
Some examples of the simple present tense are: speak, go, write, sing, play, read, walk, eat, drink, take, give, see, hear, and understand.
What are the rules for using the simple present tense?
The simple present tense is used to describe habits, unchanging situations, general truths, and fixed arrangements. It is also used to talk about scheduled future events. To form the simple present tense, use the base form of the verb (except for the verb “to be”, which is conjugated differently). For third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), add -s or -es to the base form of the verb.
How can the simple present tense be used to express habitual actions?
The simple present tense can be used to express habitual actions by using the adverbs ‘always’, ‘frequently’, ‘often’, ‘regularly’, ‘usually’, ‘sometimes’, or ‘occasionally’. For example, “I usually go to the gym on Mondays.”
How can the simple present tense be used to express facts?
The simple present tense can be used to express facts by using statements that are generally accepted as true, such as scientific facts or historical facts. For example, “The Earth rotates around the Sun” or “The American Revolution began in 1775”.