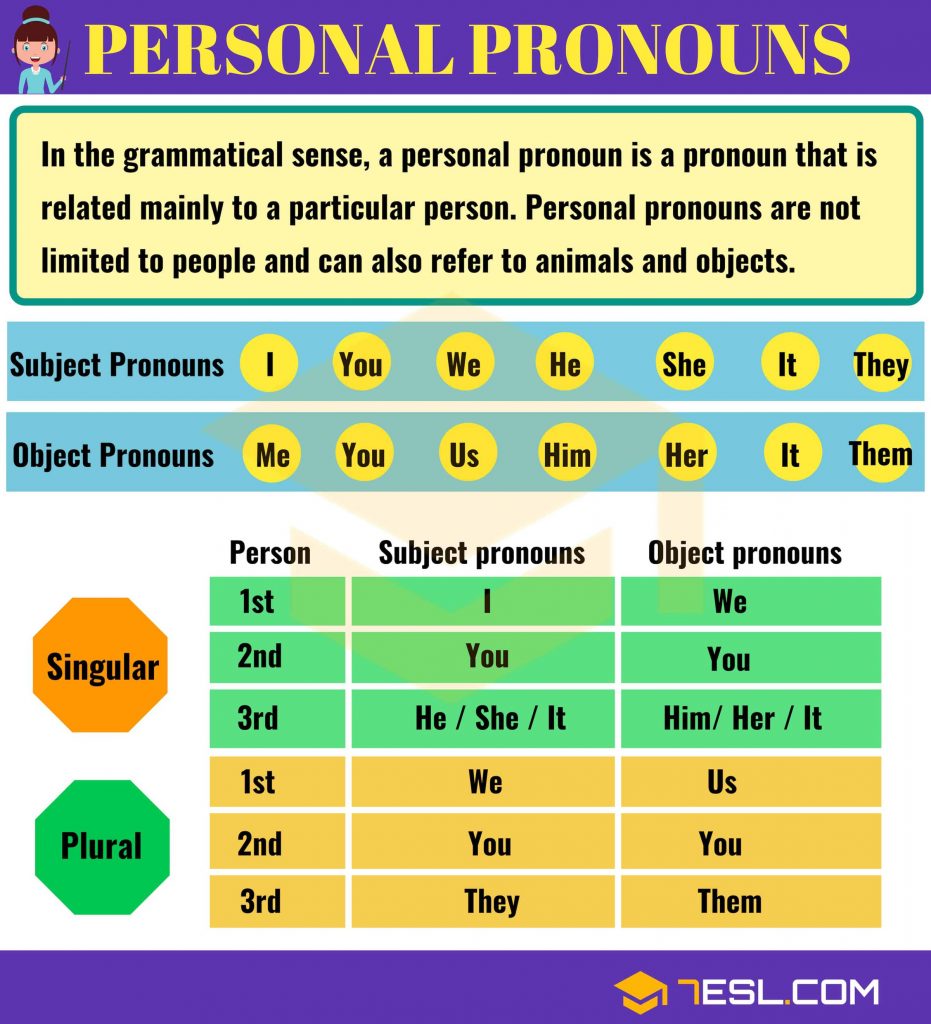
Have you ever wondered what personal pronouns are? Personal pronouns are words that can be used to refer to someone or something.
They can be used to refer to a person, place, thing, or idea. Personal pronouns can be used to show possession, to indicate a person’s gender, or to make a sentence sound more natural. They are also used to make a sentence less repetitive.
Understanding personal pronouns is important for both speaking and writing in English. In this blog, we will explore the different types of personal pronouns and how they are used in English.
Contents
Types of personal pronouns
Personal pronouns are an essential part of , used to refer to ourselves, someone else, or a thing in a sentence. A personal pronoun is a type of pronoun that refers to the person who is speaking or the person whom is being spoken to.
When we use pronouns, we are able to quickly and clearly express ideas in our writing, without cluttering the sentence with redundant words. There are different types of personal pronouns, including subjective, possessive, reflexive, and demonstrative. Subjective pronouns indicate who is speaking— I, me, you, he, him, she, hers, we, us, they, and them are all examples of subjective pronouns.
Possessive pronouns are used to show ownership— mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs are all examples of possessive pronouns. Reflexives are words that refer back to the subject of the sentence, like myself, himself, itself, ourselves, and themselves.
The last type of personal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, point to a specific object or person— this, that, these, and those are all examples of demonstrative pronouns. Using the correct personal pronoun can make a huge difference in the clarity and readability of a sentence. For example, “I threw the ball” is clearer than “Danae threw the ball” or “The person in the red shirt threw the ball.
” Without personal pronouns, it can be difficult to express ideas concisely and clearly.
Examples of personal pronouns
The use of personal pronouns is essential to building effective communication. They refer to a person or group and provide an easy way to refer directly to someone without having to name them.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the definition of personal pronouns and look at some examples. At its most basic level, the definition of personal pronouns is straightforward. They are words that substitute for nouns and point to specific people or groups.
You might recognize them from the English like I, we, you, and they. When used correctly, they provide immediacy and clarity to what we are saying or writing. Looking at some concrete examples of personal pronouns will help further our understanding of them.
Here are nine of the most common personal pronouns with some sample sentences so you can see them in action: I – “I have been to that restaurant before. ” We – “We are going to the movies tonight.
” You – “Do you want to come with us?” He/She – “He entered the room late. ” It – “It is going to rain tonight.
” They – “They are going on vacation next week. ” Me – “Mike invited me to the party.
” Him – “She gave the book to him. ” Us – “They asked us to help them. ” Using personal pronouns correctly is a great way to make your writing more efficient and easy to read. Remember, always use them to refer to specific people or groups for optimal communication.
How to use personal pronouns
When you’re writing or speaking in English, one of the most important things to remember is to use the proper personal pronoun for the subject. Personal pronouns are used to refer to people or things and make a conversation or writing sound more interesting and personal. Knowing how to properly use them is key to mastering English communication.
A personal pronoun is a word that is used instead of a person’s name or a noun in order to avoid repeating the same information. Personal pronouns in English come in three cases, singular and plural forms, and are often referred to as the subjective case (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), the possessive case (my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, theirs), and the reflexive case (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, themselves).
Each of these personal pronouns has a specific purpose and should be used in the right context in order to make your writing grammatically correct. For example, when discussing the subject of a sentence, you should use the subjective personal pronouns ‘I,’ ‘you,’ ‘he,’ ‘she,’ ‘it,’ ‘we,’ and ‘they.
’ Similarly, when talking about possession or ownership, you should use the possessive pronouns ‘my,’ ‘mine,’ ‘your,’ ‘yours,’ ‘his,’ ‘her,’ ‘hers,’ ‘its,’ ‘our,’ ‘ours,’ ‘their,’ and ‘theirs. ’ It is also possible to use the reflexive personal pronouns ‘myself,’ ‘yourself,’ ‘himself,’ ‘herself,’ ‘itself,’ ‘ourselves,’ and ‘themselves’ to add an extra dimension to a sentence. Personal pronouns can add clarity, brevity, and personality to your writing, making it easier to understand.
When used correctly, they help to avoid confusion and provide an opportunity to engage with the reader in a more meaningful way. To truly master the English , it is important to learn to use personal pronouns correctly.
Common mistakes with personal pronouns
When it comes to using pronouns, it can be easy to make mistakes. Personal pronouns, often found in a variety of different contexts, can be misunderstood and used incorrectly. Understanding what personal pronouns are, as well as their different forms, can help to reduce errors when using them.
Personal pronouns are essentially nouns that are used in place of other nouns, such as ‘he’ and ‘she’ instead of names like ‘John’ or ‘Amy’. They can be used to refer to a person or thing and come in two main forms: singular and plural.
Singular pronouns are used when referring to one person, such as ‘he’ and ‘she’, and plural pronouns are used when referring to more than one person such as ‘they’ and ‘we’. It’s important to note, however, that personal pronouns have both a gender-specific and gender-neutral form.
For example, ‘they’ and ‘them’ can be used to refer to a single person, regardless of gender. Similarly, ‘she’ and ‘he’ can be used to refer to a group of people who identify with either gender. Making sure that you use the correct pronoun for the context is essential.
Misusing a personal pronoun can lead to misunderstood meaning, confusion, and even offense. For example, using the singular ‘they’ to refer to a female friend could be taken as insensitive. In situations where you’re unsure of a person’s gender, it’s best to simply use a person’s name or a gender-neutral pronoun.
Understanding the different forms of personal pronouns and their usage can help you avoid mistakes and use the right personal pronouns to get your meaning across.
Our video recommendation
Bottom Line
Personal pronouns are words used to refer to oneself or others, such as “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” “we,” “they,” and so on. They are used in place of a person or thing’s name to avoid repetition and make sentences clearer and more concise. Personal pronouns are an important part of speech and are used in almost every sentence.
FAQ
What is the definition of personal pronouns?
Personal pronouns are pronouns that refer to a particular person or group of people, such as I, me, you, he, she, it, we, us, they, them, etc.
What are the different types of personal pronouns?
The different types of personal pronouns are: first person (I, me, mine, we, us, ours), second person (you, yours), and third person (he, she, it, they, them, his, her, hers, its, their, theirs).
How are personal pronouns used in a sentence?
Personal pronouns are used to refer to people or things without having to use their names. Examples of personal pronouns include I, me, you, he, she, it, we, us, they, and them.
What is the difference between personal pronouns and possessive pronouns?
Personal pronouns refer to people or things in a sentence and indicate the person speaking (I, you, he, she, it, we, they) while possessive pronouns indicate ownership or possession (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs).
How do personal pronouns change depending on the context?
Personal pronouns change depending on the context according to the person being referred to (first, second, or third person), the number of people being referred to (singular or plural), and the gender of the person being referred to (male, female, or gender-neutral).
What are the rules for using personal pronouns?
The rules for using personal pronouns are as follows: 1. Use the subject pronoun when the pronoun is the subject of the sentence. 2. Use the object pronoun when the pronoun is the object of the sentence. 3. Use the possessive pronoun when the pronoun is showing possession. 4. Use the reflexive pronoun when the pronoun is referring back to the subject of the sentence. 5. Use the intensive pronoun when the pronoun is used to emphasize the subject of the sentence.