Are you looking for an introduction to the rules and examples of cases of pronouns? Look no further! In this blog, we will explore the various rules and examples of cases of pronouns, so that you can gain a better understanding of this important grammar concept.
We will discuss the different types of pronouns, the different cases they can take, and provide examples of each. We will also discuss the importance of understanding pronoun cases and how they can help you become a better communicator.
So, let’s get started!
Contents
Types of pronouns
. The study of pronouns is a fundamental part of .
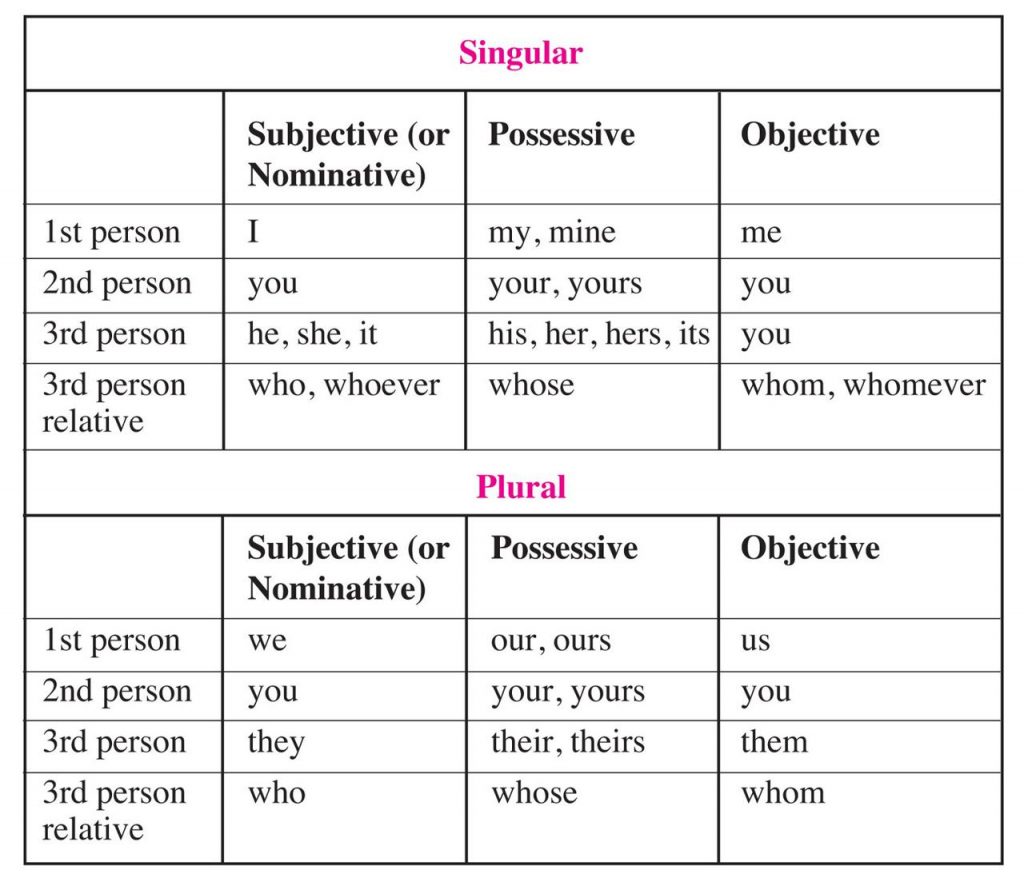
Cases of pronouns are an essential part of a and are used to denote the relationship between the subject and object in a sentence. In English , there are four primary cases of pronouns: nominative, possessive, objective, and reflexive, with each possessing distinct rules and usage. Nominative case pronouns are used as a subject of a sentence.
They are often followed by a verb; for example, “he” in “He loves her”, or “I” in “I am happy”. Nominative pronouns are typically singular and take the place of a person or thing that is performing an action. Possessive case pronouns, also known as possessive adjectives, describe nouns in terms of ownership or possession.
“His”, “Her”, or “Theirs” are examples of possessive case pronouns. These pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to a particular person, such as “This is her book” or “This book is his”.
Objective case pronouns are used as objects of verbs. Examples of objective pronouns include “me”, “her”, “him”, and “us”. They are often used as the recipient of an action, such as in “She loves me” or “They need us”.
Finally, reflexive case pronouns are pronouns that reflect back onto the subject of the sentence. These pronouns always end in -self, such as “myself”, “himself”, and “herself”.
These pronouns are used when the subject of the sentence is acting upon itself. For instance, “She taught herself Spanish” or “The child is looking at himself in the mirror”. Overall, cases of pronouns are used in the English to denote the relationship between the subject and the object in a sentence. Understanding these cases and the associated rules can help us become more confident in our usage and expression of the .
Rules for using pronouns
Proper pronoun use is essential to create clear, successful sentences. Whether you are writing an essay, a blog or a business memo, correct pronoun usage will make your writing stand out as professional and clear. To make sure you’re correctly using pronouns in all your documents, here are a few rules to know.
Pronouns are usually used in place of a noun; this allows us to reuse a noun without repeating it. For example, rather than saying, “John went to the store and John bought some bread,” we can simply use the pronoun “he” and say, “He went to the store and bought some bread.
” Pronouns can also be used to refer to a noun, even when it’s not present in the sentence. To correctly use a pronoun, you must first determine the case you need. The two main pronoun cases are subjective and objective.
For example, pronouns like “he,” “she,” and “it” are known as subjective pronouns because they refer back to a person who is performing a verb. On the other hand, pronouns like “him,” “her,” and “it” are called objective pronouns because they refer to persons or things who receive the action of a verb.
For example, suppose there are two people, Alice and Bob. If Alice hands Bob a book and says, “Keep it warm for me,” then “she” is the subjective pronoun since Alice is the one performing the action, and “it” and “him” are the objective pronouns since Bob is the one receiving the action.
Knowing when to use the correct case of a pronoun can make all the difference in writing effective sentences. To make sure your sentences are correct, check the pronoun case against the noun it’s referencing. For example, if you’re referring to Alice, make sure you’re using “she” and not “her”.
Likewise, if Bob is the one being referenced, you should use “him” and not “he. ” With this simple trick, you’ll never go wrong when using pronouns!
Examples of pronouns in sentences
Pronouns play an important role in speech and writing. They are used to refer to people, places, and things, often replacing nouns for added emphasis and to make sentences more succinct. In English, there are five cases of pronouns, each with different rules and examples to help you easily identify and use them.
The five cases of pronouns are subjective (or nominative), objective, possessive, reflexive, and intensive. Each of these cases serves a distinct purpose, and each has its own rules for usage and examples.
Understanding the five cases of pronouns is essential for writing and speaking clearly and effectively. The subjective case of pronouns refers to pronouns that simply replace a noun without an object or possessive case in the sentence. Examples of the subjective case would include the pronouns “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” “we,” “they,” and “who.
” For example, “John is an intelligent person,” is replaced with “he is an intelligent person. ” The objective case of pronouns refers to when a pronoun is used as the direct object of a verb, or by a preposition.
Examples of the objective case would include “me,” “you,” “him,” “her,” “it,” “us,” “them,” and “whom. ” For example, when the sentence “John saw a movie” is changed to “He saw it,” “it” is the objective pronoun.
The possessive case of pronouns is used to indicate that something belongs to an individual. Examples of the possessive case would include “mine,” “yours,” “his,” “hers,” “its,” “ours,” and “theirs. ” For example, when the sentence “The house belongs to John” is changed to “The house is his,” “his” is the possessive pronoun.
The reflexive case of pronouns is used with reflexive verbs and to emphasize a noun or pronoun. Examples of the reflexive case would include “myself,” “yourself,” “himself,” “herself,” “itself,” “ourselves,” “yourselves,” and “themselves. ” For example, when the sentence “John hurt himself” is changed to “He hurt himself,” “himself” is the reflexive pronoun. The intensive case of pronouns is used to give emphasis to a noun or pronoun. Examples of the intensive case would include “myself,” “yourself,” “himself,” “herself,” “itself,” “ourselves,” “yourselves,” and “themselves. ” For example, when the sentence “John himself cooked breakfast” is changed to “He cooked breakfast himself,” “himself” is the intensive pronoun. Understanding the rules and examples for the five cases of pronouns is an essential part of mastering the English . Having an understanding of their different meanings and usages will help you more effectively communicate your thoughts and feelings in writing and speaking.
Common mistakes with pronouns
Pronouns can be a tricky subject for English learners. The different cases and rules of English pronouns can be difficult to understand.
A teacher can provide guidance to ensure students can use pronoun cases correctly. The three most common pronoun cases are subject, object, and possessive. Each case dictates how the pronoun should be used in a sentence.
When the pronoun acts as a subject of the sentence, it is in subject case. For example, “She walked to the store.
” In this sentence, “she” is the subject of the sentence, so it is in subject case. The same rule applies for pronouns that act as objects in the sentence. For example, “She gave it to him.
” In this sentence, “him” is the object, so it is in object case. Finally, when a pronoun shows possession, it is in possessive case. For example, “Her book was on the table.
” In this sentence, “her” is the possessive pronoun, so it is in possessive case. It is important to remember that the cases of these pronouns change depending on the context.
For example, “She gives him the book” uses both “she” and “him” in subject case, since they are both subjects of the sentence. But in “She gave him the book,” “she” is in subject case, and “him” is in object case, since “him” is the object of the sentence. Teachers can help their students become comfortable with the different cases of pronouns by providing specific examples, and by having their students practice using all the different cases in their sentences. With the right guidance and practice, students can confidently use the correct cases of pronouns in their writing and conversation.
Our video recommendation
Conclusion
This article provides an overview of the rules and examples of pronoun cases, which are the forms of pronouns used in different grammatical contexts. It explains the three cases of pronouns – subjective, objective, and possessive – and provides examples of each.
It also provides tips on how to correctly use pronouns in sentences.
FAQ
What are the rules for using pronouns in a sentence?
When using pronouns in a sentence, make sure they agree with the noun they are replacing in terms of gender, number, and person. Additionally, pronouns should be placed as close as possible to the noun they are replacing.
What are the different types of pronouns?
The different types of pronouns include personal pronouns (e.g. I, you, he, she, it, we, they), possessive pronouns (e.g. mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs), reflexive pronouns (e.g. myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, themselves), demonstrative pronouns (e.g. this, that, these, those), interrogative pronouns (e.g. who, whom, which, what), relative pronouns (e.g. who, whom, which, that), and indefinite pronouns (e.g. all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, neither, nobody, no one, nothing, one, other, some, somebody, someone).
How do you identify the subject of a sentence using pronouns?
To identify the subject of a sentence using pronouns, look for the pronoun that is performing the action of the sentence.
What are the different cases of pronouns?
The different cases of pronouns are nominative, possessive, objective, and reflexive.
What are some examples of pronouns in a sentence?
Examples of pronouns in a sentence include: he, she, it, they, them, us, we, him, her, his, its, our, yours, and theirs.
How do you determine the correct pronoun to use in a sentence?
The correct pronoun to use in a sentence should agree with the noun it is referring to in terms of gender and number. For example, if the noun is singular and feminine, the pronoun should be “she” or “her”; if the noun is plural and masculine, the pronoun should be “they” or “them”.