Learning about prepositions of direction can help you to better understand how to express yourself in English. These words are used to describe the relationship between two objects, and can be used to talk about movement from one place to another. Whether you’re a student, traveler, or professional, understanding prepositions of direction will help you communicate more effectively.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss the various prepositions of direction, their meanings, and how to use them in a sentence. We’ll also provide examples of each preposition in action to help you better understand how to use them.
So let’s get started and explore the prepositions of direction!
Contents
Types of prepositions of direction
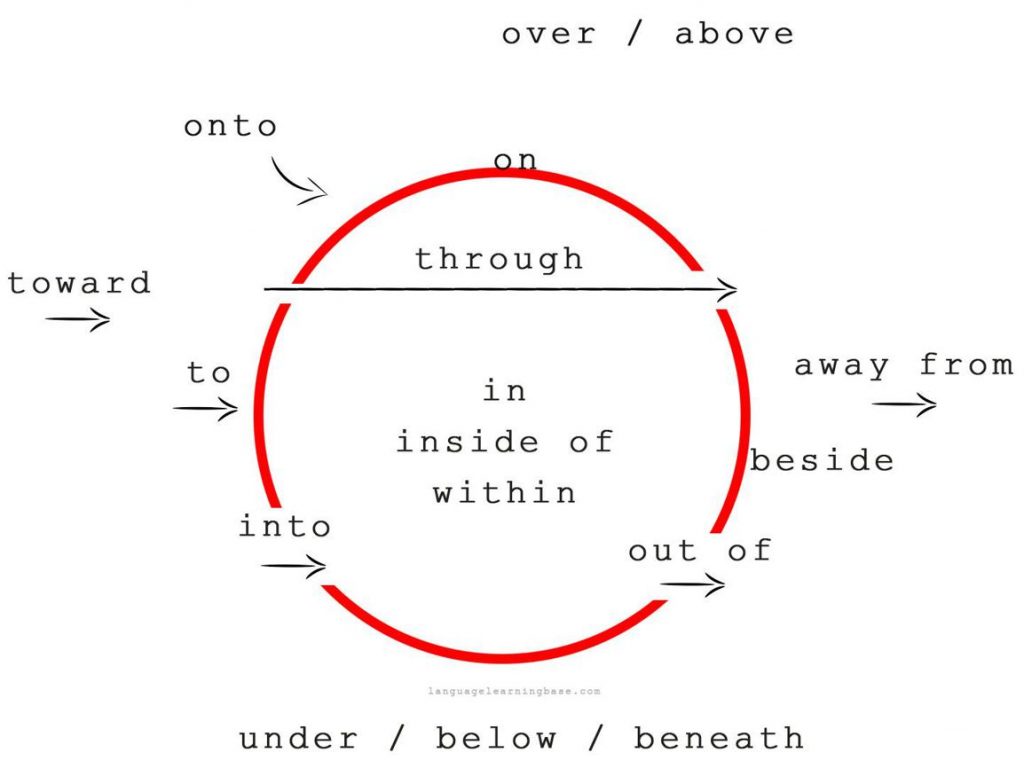
Prepositions of direction are an important grammatical tool to describe movement in a sentence. These simple words are incredibly versatile and can describe motion in both physical and figurative senses. The basic prepositions of direction are: to, from, in, on, up, down, over and under.
These words are generally used in pairs to show direction of movement and context, such as going to, coming from, moving in, falling on, running up, walking down, flying over and crawling under. They can all be used to express the place something is arriving or departing from, or the direction it is heading in.
Using prepositions of direction can be a good way to be more precise in describing a location, person or thing’s movements. For example, ‘He walked to the door’ is much more expressive than simply ‘He walked’, as it describes the path or specific direction he took.
They can also be used to show purpose, such as in ‘He ran to the store’, where ‘to’ conveys his purpose in taking the action. In some contexts prepositions of direction can also be used to give an indication of time. For instance, you might say ‘He’s been in and out of school all day’, to mean he’s been coming and going from school all day.
To increase the effectiveness of your writing and make it more descriptive, try to use prepositions of direction wherever you can. They are a great tool for adding clarity and detail to your sentences.
Examples of prepositions of direction
Prepositions of direction are naturally used when we talk about how to get from one place to another, talk about directions and even when giving instructions. Understanding how to use these small words can help you accurately communicate with your peers, coworkers, and colleagues.
Prepositions of direction are specifically used when you want to talk about a direction, either physical or metaphorical. Examples of these might include “up,” “down,” “on,” “off,” “along,” “into,” “over,” “under,” “through,” and “across. ” Each of these words has a specific purpose and helps to give details about a physical direction or motion.
The preposition of direction is often used in questions. For example, someone might ask “Where do I go from here?” To answer that question accurately, one could say “Turn to the left, go straight for five blocks, then turn right.
” This answer provides clear directions that can be followed in order to reach the desired destination. Another example might be “I am looking for the post office; do I turn right or left?
” In this question, the listener would take note of the preposition of direction in order to answer the question. It is important to note that prepositions of direction can be used metaphorically, as well.
A metaphor is a comparison between two unrelated things, so this could often be seen in the context of context like “I am climbing the ladder of success” or “I am stepping off the beaten path. ” As you can see, prepositions of direction are incredibly versatile and can be used in various contexts with ease. In conclusion, understanding prepositions of direction is an important part of being able to communicate effectively.
Knowing how to identify and use them correctly can help to ensure that you are providing accurate directions or information, both physically and metaphorically. By understanding the nuances of using prepositions of direction, you will be able to confidently and accurately communicate your message.
Common mistakes with prepositions of direction
Prepositions of direction are an area of grammar that many English learners struggle with, and they often make a lot of errors when using them. Even native speakers can make mistakes when using these prepositions, so it’s important to get this right. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the most common mistakes with prepositions of direction and provide some examples to help you understand how they should be correctly used.
When using prepositions of direction, the most common mistake is to use the wrong preposition. For example, people tend to use ‘in’ instead of ‘into’ or ‘onto’ instead of ‘on’.
It’s important to be aware of how these prepositions change depending on the place and the movement. Let’s take a look at some examples. If you want to indicate movement from one place to another, you’ll need to use the preposition ‘into’.
The preposition ‘into’ indicates that the movement is going towards a place. For example, if you were talking about a person going from their house to the store, you could say “She went into the store.
” If you were talking about a ball rolling onto a roof, you would say “The ball rolled onto the roof. ”On the other hand, if you’re talking about motion that is staying within a place, you should use the preposition ‘in’. For example, if you were talking about a person walking around in the store, you would say “She walked in the store.
” If you were talking about a ball rolling around on the roof, you would say “The ball was rolling around on the roof. ”These are the two primary mistakes that people make when using prepositions of direction.
It’s important to be conscious of which preposition to use in the right context in order to make yourself understood clearly. By understanding the differences between these prepositions and using them properly, you can improve your English fluency.
Tips for using prepositions of direction
Prepositions of direction are small but powerful words that provide direction, making it possible to connect two different objects, concepts, or events to each other. While mastering the English can be challenging, learning how to properly use prepositions of direction is a great way to help improve your English skills. In this blog post, I will provide tips and suggestions on how to incorporate these prepositions into your writing.
The most common prepositions of direction in English are ‘to’, ‘into’, ‘onto’, ‘from’, ‘by’, ‘over’ and ‘through’. While you could simply remember each preposition for their specific usage, it’s best to try to understand what each word means.
To helps describe the destination or end of a movement, ‘into’ refers to something going into or onto another object, ‘onto’ is used to show a movement from one place to another, ‘from’ is used to indicate the origin of a movement, ‘by’ indicates a means of transportation, ‘over’ indicates movement across a barrier, and ‘through’ indicates movement with a barrier in the way of the movement. To make sure you are using prepositions of direction correctly, be sure to treat each phrase as its own separate entity.
For example ‘I am flying from London to New York’ is looking at the phrase as the whole unit, but when broken down into its separate entities, ‘I am flying’ is the movement, ‘from London’ is where the activity is starting, and ‘to New York’ is the destination of the movement. This way of looking at phrases can also be extended to other phrases such as ‘He ran into the store’ where you would be looking at the individual phrases of ‘He ran’ being the movement, ‘into’ stating what direction he ran, and ‘the store’ saying where he went. With continued practice and understanding, soon you will be able to navigate prepositions of direction with ease when writing or speaking your sentences.
Treating each phrase as its own unit to understand the relationship between the two objects and direction can be a great help. Following these tips, you can be sure to make great strides in your understanding and use of prepositions of direction.
Our video recommendation
Final Touch
This article discussed the different prepositions of direction and their uses. It provided examples of each preposition, including ‘in’, ‘on’, ‘at’, ‘to’, ‘from’, ‘into’, ‘onto’, ‘through’, ‘over’, and ‘under’. It also discussed the difference between movement and direction, and how the prepositions can be used to indicate either.
Finally, it emphasized the importance of using the correct preposition for the context.
FAQ
What is the difference between a preposition of direction and a preposition of place?
A preposition of direction is used to describe the movement of an object from one place to another, such as “up,” “down,” “over,” “under,” etc. A preposition of place is used to describe the location of an object, such as “in,” “on,” “at,” etc.
What are some common prepositions of direction?
Some common prepositions of direction are: up, down, in, out, over, under, away, towards, through, around, across.
How do prepositions of direction help to describe movement?
Prepositions of direction help to describe movement by providing a specific direction in which something is moving, such as up, down, left, right, forward, backward, etc. They can also provide a sense of distance, such as near, far, close, away, etc.
How can prepositions of direction be used in a sentence?
Prepositions of direction can be used to indicate the movement of an action or object in a sentence. For example, “She walked up the stairs” or “The ball rolled down the hill”.
What are the rules for using prepositions of direction?
The rules for using prepositions of direction are to use “to” when referring to a specific destination, “toward” when referring to a general direction, and “into” when referring to entering a place.
How can prepositions of direction be used to describe a location?
Prepositions of direction can be used to describe a location by indicating the direction and movement between two points. Examples include: to, from, up, down, over, under, through, across, along, around, and into.